Facial Baroparesis
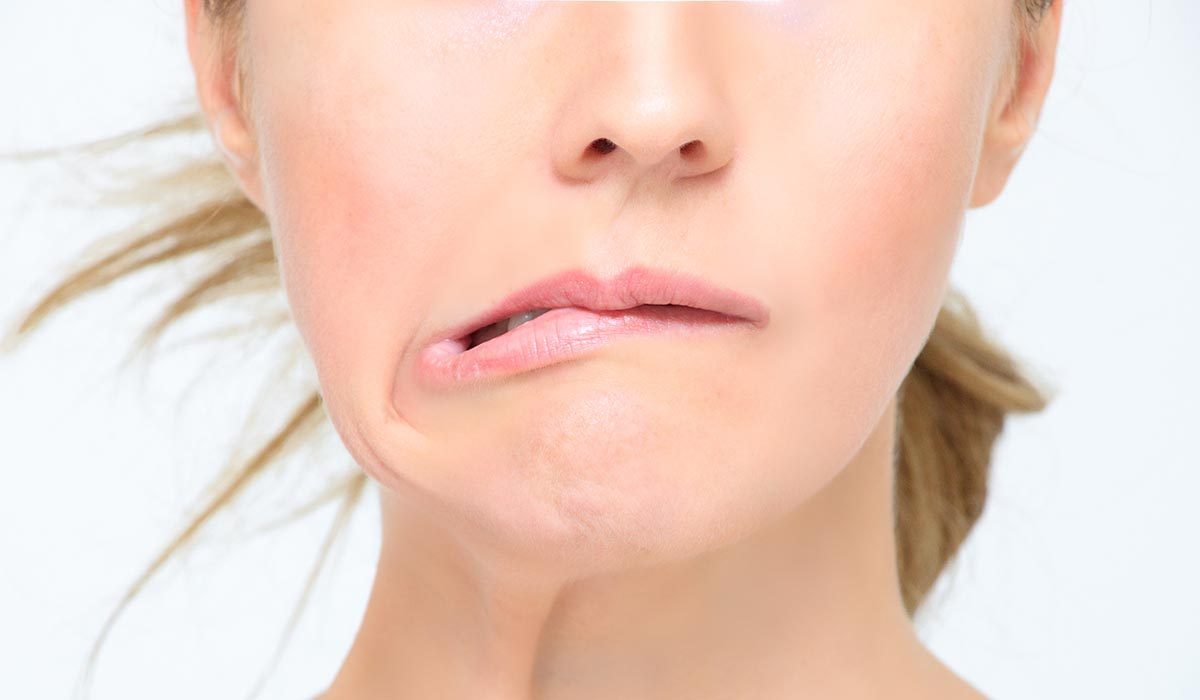
Facial baroparesis is a reversible paralysis of the facial nerve due to increased pressure in the middle ear when ascending from scuba diving. This tends to recur with repeated diving, but does go away after several hours.
Alternobaric Vertigo
Alternobaric vertigo happens when there is unequal pressure in each ear. Prevention and management while diving will help keep you safe.
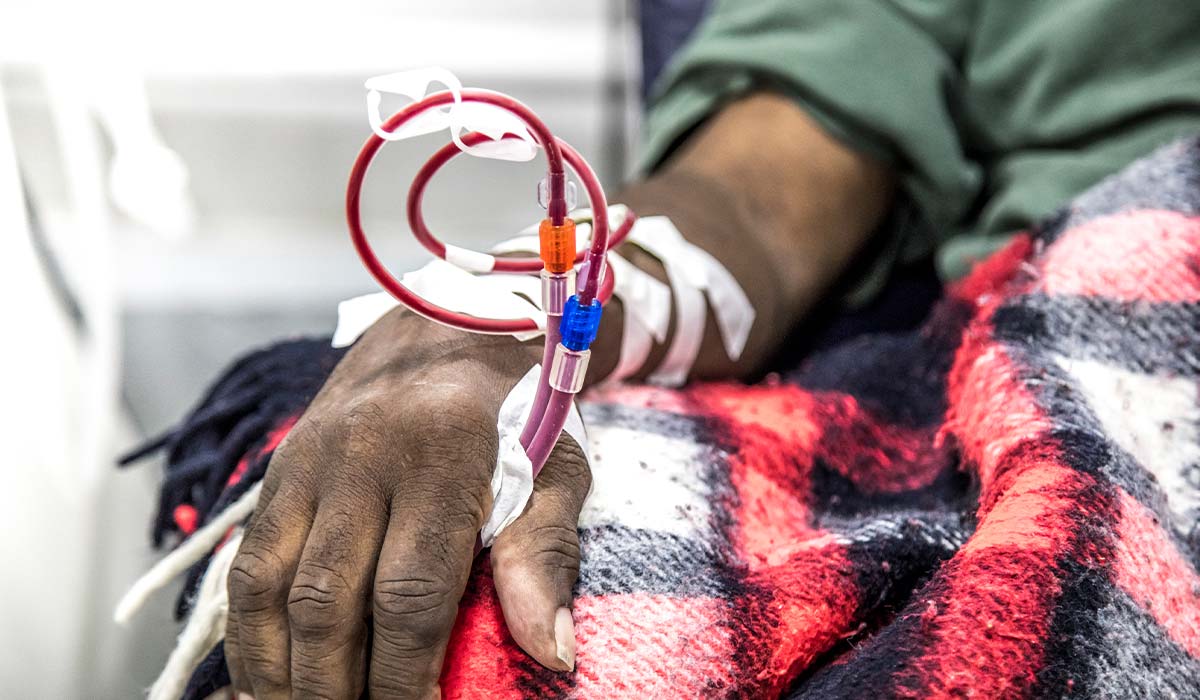
Dialysis and Diving
Overview Dialysis is the common name for renal replacement therapy. This therapy is indicated when their kidneys suddenly stop working, or when there is a gradual decline in kidney function […]
Over-the-Counter Medications
It is very common to take an over-the-counter (OTC) medication without any thought to the side effects. Even common ones like antihistamines, decongestants, pain relievers, and motion sickness medications can have side effects. If you are considering diving while using one of these drugs, the side effects could be even more powerful than when on land and increase your risk of an injury.
Cardiovascular Medications and Diving
Cardiovascular medications are available to treat certain conditions, however, they can influence someone’s ability to dive safety. Read more about certain medications and their implications in diving.
Oxygen Toxicity
As partial pressure increases, protective mechanisms are slowly overwhelmed and biochemical reactions are affected. This may eventually result in oxygen toxicity.
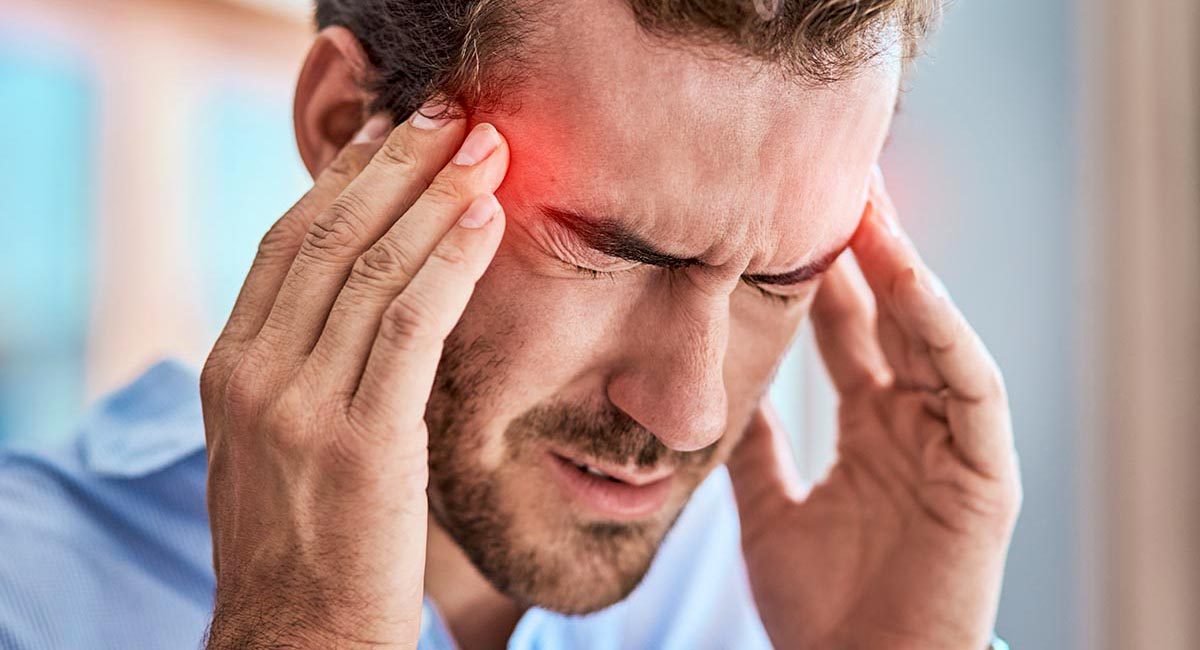
Headaches and Diving
Headaches happen to everyone, but when they happen regularly to divers it may be time to track down the cause. Learn some of the possible causes of frequent headaches and some quick-fix solutions.
Pregnancy and Diving
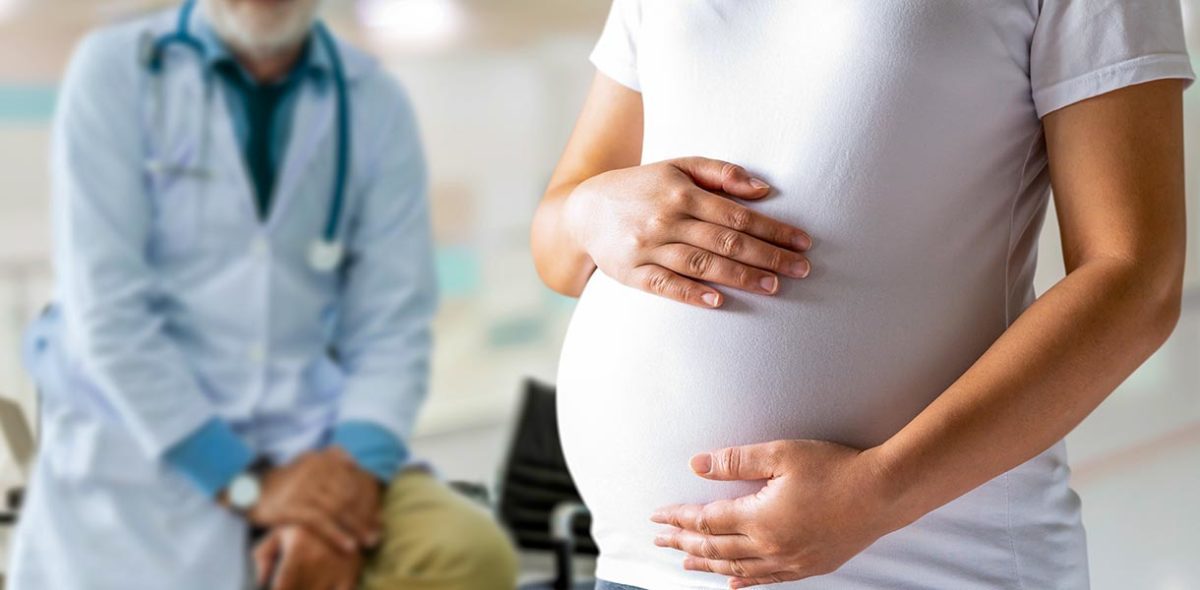
Most divers can recall from their open water training that women are encouraged to stop diving during pregnancy, but few classes go into further detail. What are the risks of diving while pregnant?
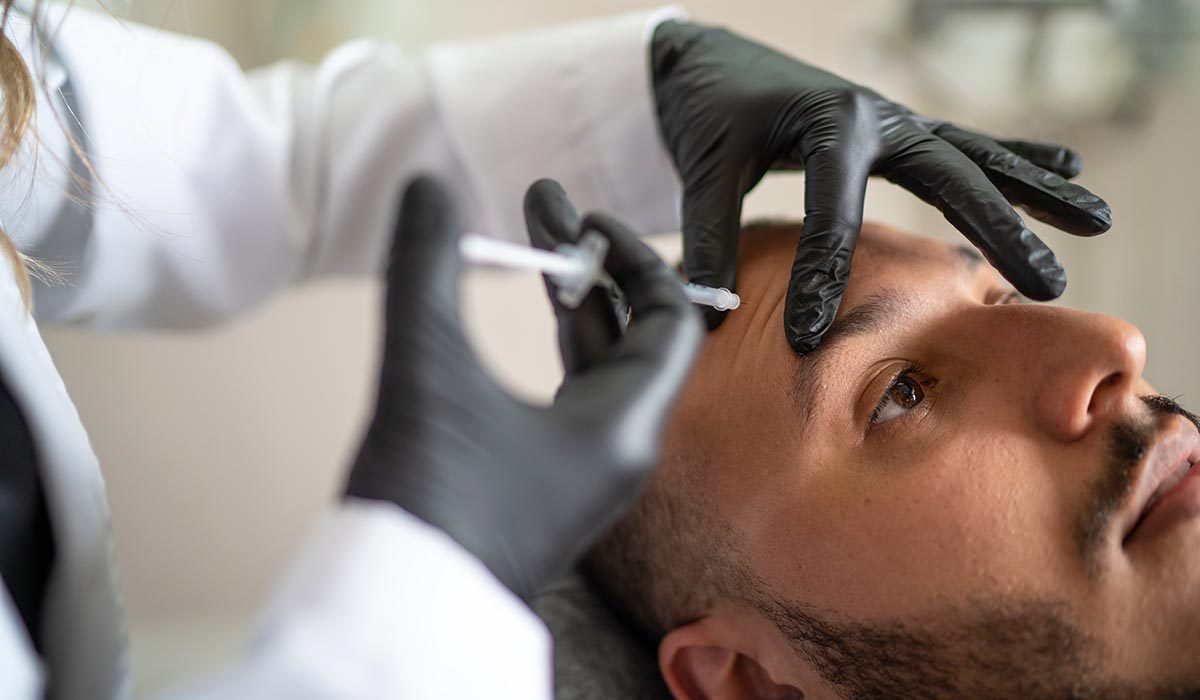
Noninvasive Plastic Surgery
A person could elect for a noninvasive plastic surgery procedure for a number of reasons, but they all involve some amount of recovery time and risk. And, it’s important to note how long someone must wait before returning to diving.
Blood Thinners & Diving
Blood thinners are the common name of a number of groups of drugs and chemical substances that can prevent or reduce the coagulation of blood. Learn about blood thinners and their implications in diving.