Decompression Illness
Decompression illness (DCI) encompasses two conditions: decompression sickness (DCS) and arterial gas embolism (AGE). Symptoms of DCI include numbness and tingling, pain in the joints or muscles, fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath and more.
Flying After Diving
Flying after diving can increase the risk of decompression sickness (DCS) because of the relative decrease in ambient pressure with altitude. Here’s how to lower your likelihood of DCS and ensure your safety during your next flight.
Anxiety: Is It a Contraindication to Diving?
Anxiety is a mental health condition that refers to an overwhelming sense of apprehension or fearfulness. Anxiety can produce both psychological and physical symptoms that may be relevant in diving.
Hypertension
Hypertension is a common medical condition in both the general population and among divers. Hypertension affects people differently, and not everyone knows they have it. Certain medications may have implications for diving.
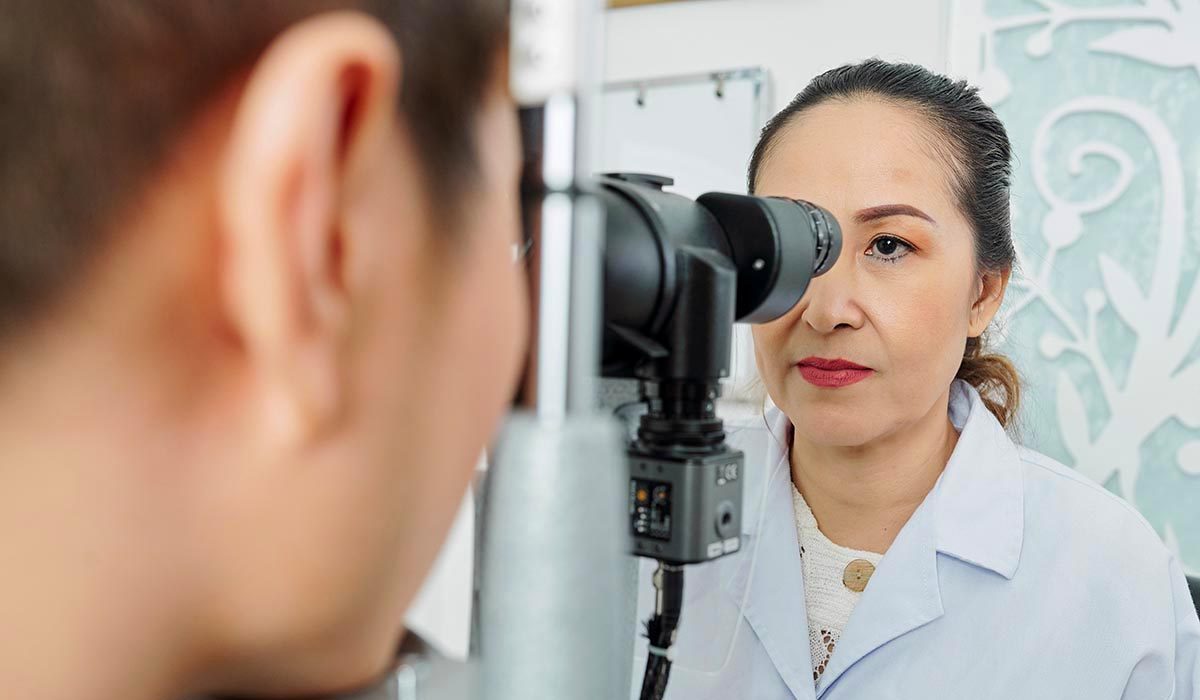
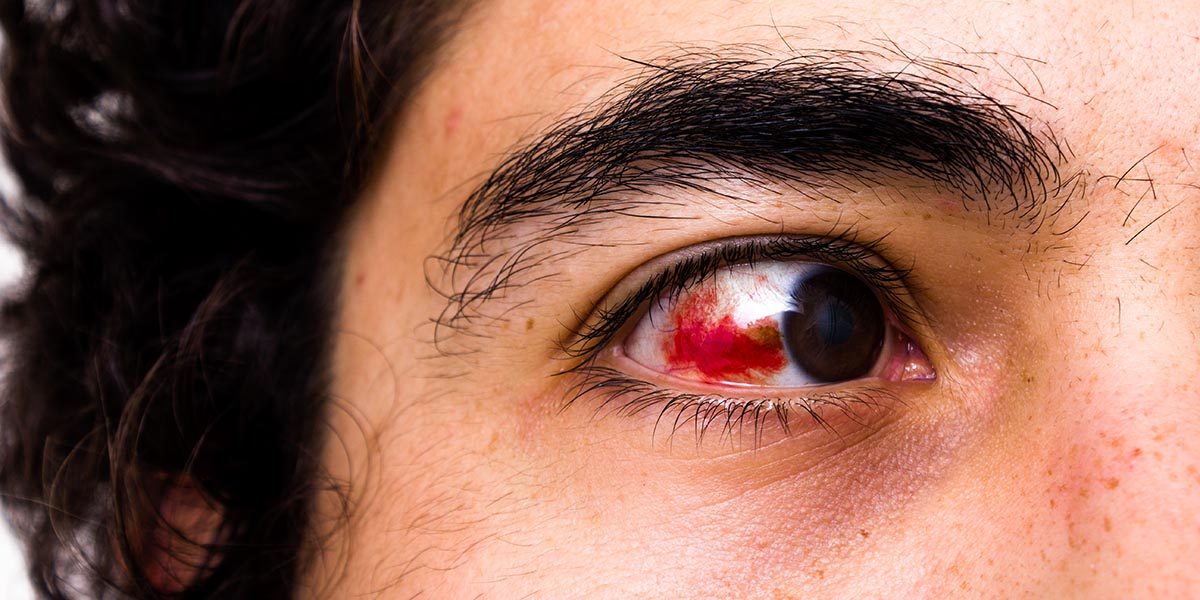
High-Pressure Ophthalmology
Diving exposes the eyes to increased pressure. While most of the time this has little or no negative effects on the diver, problems are possible. Learn more about how cataract surgery, glaucoma and other eye-related concerns may affect diving.
Mask Squeeze (Facial Barotrauma)
Failure to properly equalize the air space in your mask may result in an injury to the face and/or one or both eyes. Common among new divers, this condition can be avoided with attention to equalization while diving.
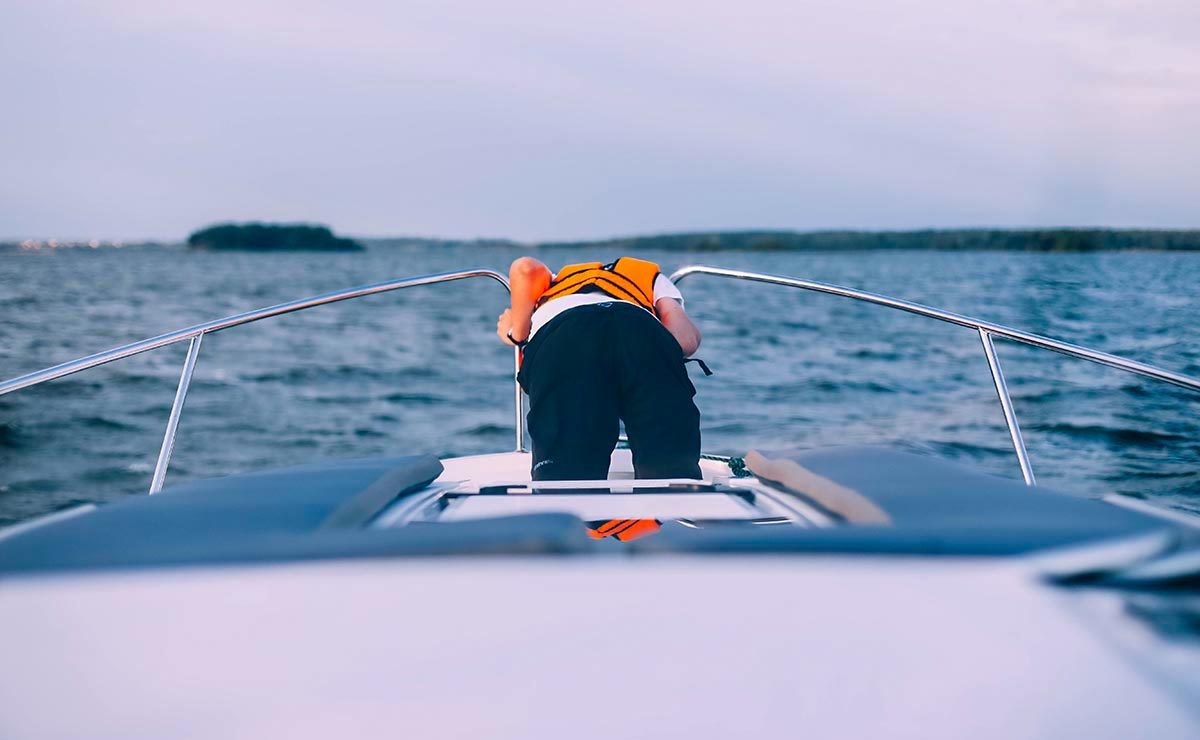
Motion Sickness
Motion sickness, or seasickness, can happen to anyone. When the inner ear sends signals to the brain that differ from those sent from the eyes, this can lead to dizziness, nausea and vomiting. Fortunately there are many options for managing the condition.
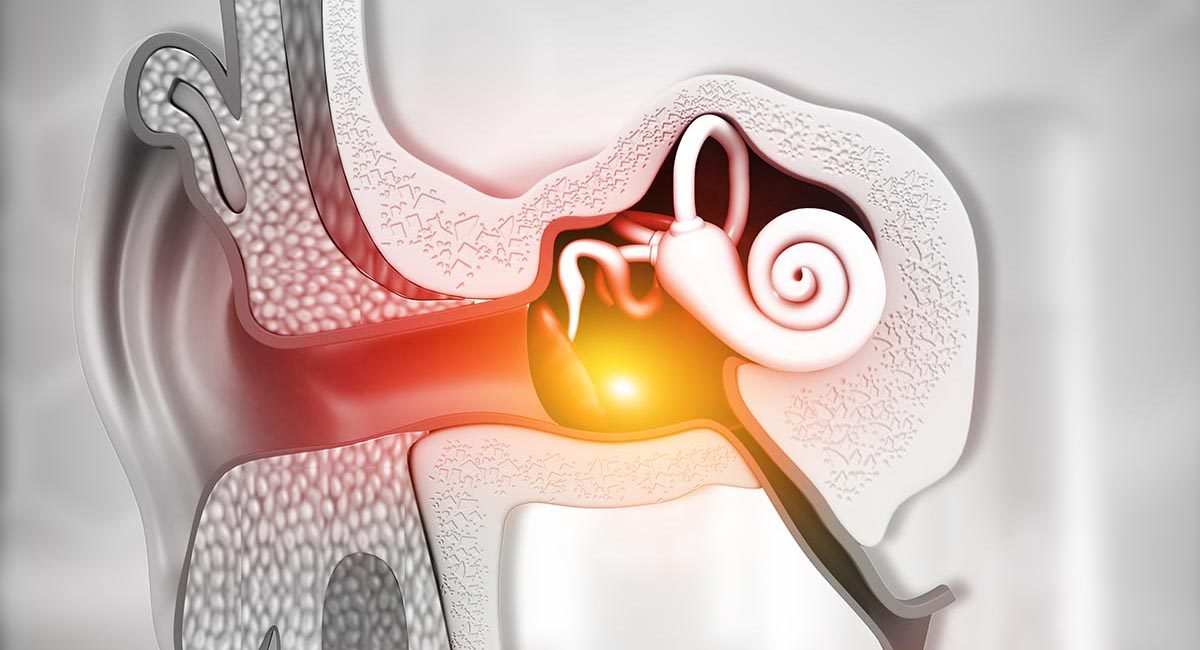
Middle-Ear Equalization
Middle-ear equalization is an essential skill for divers. Understanding how pressure changes affect the air spaces in your ears and sinuses will aid your understanding of how the various equalization techniques work.
Middle-Ear Barotrauma (MEBT)
Middle-ear barotrauma (MEBT) is common in diving, but with proper precautions it can be avoided. Learn the symptoms, prevention strategies and proper first aid techniques for this troublesome underwater ailment.
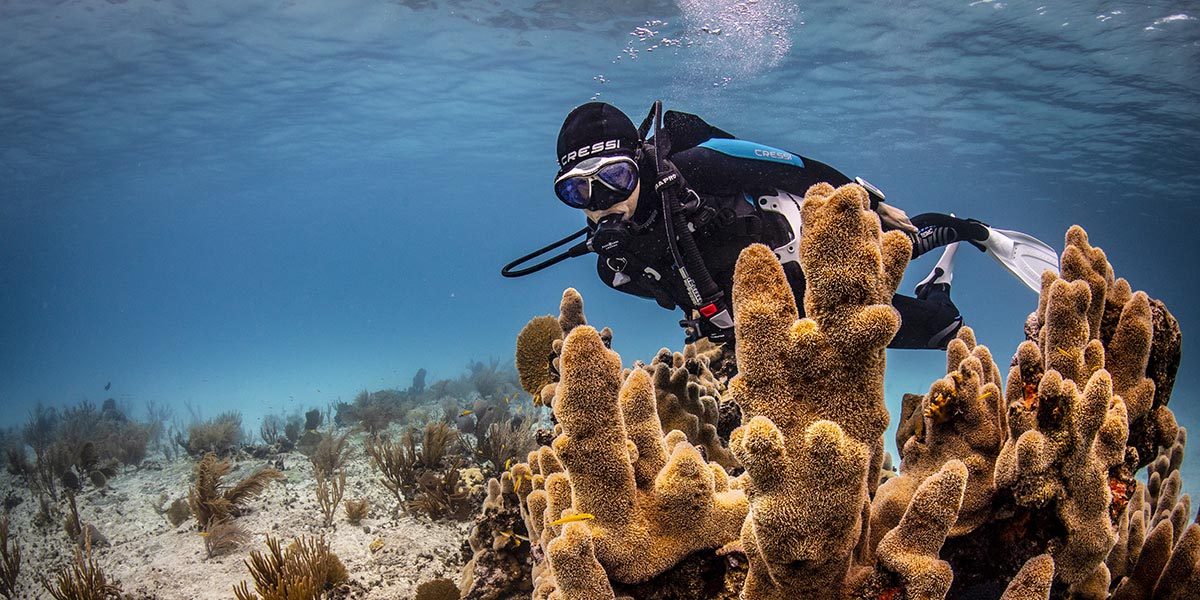
Coral Scrapes and Cuts
Skin abrasions in marine environments can be more challenging to treat than those that occur on land. Avoid contact with coral, but learn proper wound care so you’ll know what to do in the event of a coral scrape.